The sixth in a seven-part series
Think ahead 10 or 15 years and ask yourself, “What proportion of the activity called ‘learning’ will be located in the institution called ‘school’?” The availability of relatively cheap technologies offering direct access to knowledge of all types creates opportunities for students to experience a dramatic increase in the choice of what they learn, with whom they choose to learn, and how they choose to learn. How will the institution called “school” survive in this environment, in what form will it survive, and what would schools look like if they chose not just to “survive” but to find a productive place in this new environment?
With rare exceptions, schools currently treat the digital revolution as if it never happened. Computers, more often than not, still sit in dedicated rooms, accessible only with adult supervision. Laptops, when they are used at all in classrooms, are frequently employed as electronic worksheets, digital typewriters, and presentation producers, rather than as extensions of students’ access to knowledge. When students do use technology to extend the reach of their learning, they typically do so by visiting predigested information sources and cutting and pasting information into predetermined, teacher-driven formats. “Social networking” among students is treated as a subversive activity engaged in by kids who are up to no good, and certainly not as a promising point of entry to anything that might be called “learning.”
When students step out the door of the institution called school today, they step into a learning environment that is organized in ways radically different from how it once was. It’s a world in which access to knowledge is relatively easy and seamless; in which one is free to follow a line of inquiry wherever it takes one, without the direction and control of someone called a teacher; and, in which, with a little practice, most people can quickly build a network of learners around just about any body of knowledge and interests, unconstrained by the limits of geography, institutions, and time zones. If you were a healthy, self-actualizing young person, in which of these environments would you choose to spend most of your time?
The basic problem with this scenario, however, is this: The more accessible learning becomes through unmediated relationships and broad-based social networks, the less clear it is why schools, and the people who work in them, should have such a large claim on the lives of children and young adults, and the more the noneducational functions of schooling come to the fore.
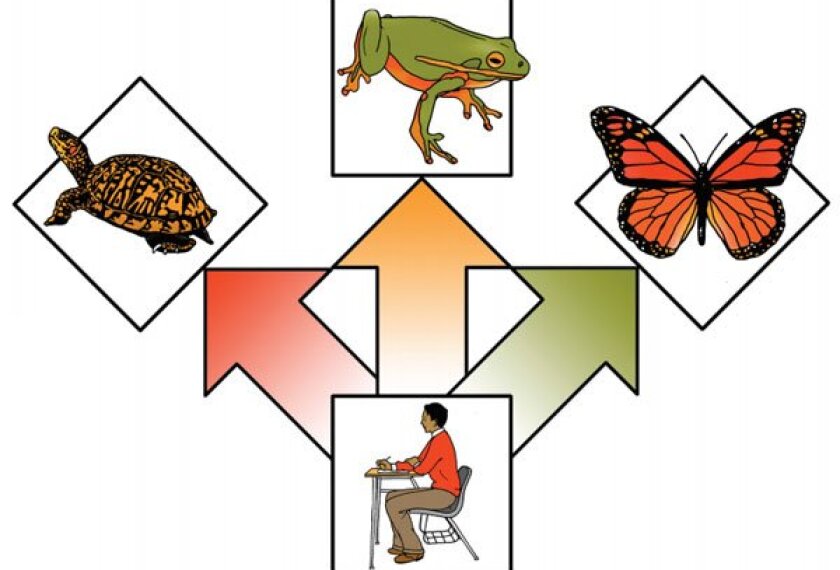
Consider three possible school scenarios for the next generation or so.
The first might be called “fighting for survival,” or “turtle gets a laptop.” 69��ý continue to be organized and run in much the same way as they are today. They “incorporate” various forms of learning technology into their existing organization and culture—more laptops, more interactive whiteboards, faster Internet connections, more digital lessons, and greater use of technology for improved efficiency of operations (grading, parent communication, coordination of meeting times, and so on). Teachers and schools continue to control access to content and learning. In this instance, schools will increasingly become custodial institutions, isolated from the lives of their students and the learning environment beyond their walls.

A working group on the “Futures of School Reform,” organized by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and led by Robert B. Schwartz and Jal D. Mehta of Harvard and Frederick M. Hess of the American Enterprise Institute, includes more than two dozen researchers, policymakers, and practitioners from around the country. The group is seeking to engage a wider audience in an “urgent” conversation—one that it hopes can advance the national dialogue on improving public education for all children. The working group has received convening support from the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation and the Spencer Foundation.
Education Week is running a seven-part series of Commentary essays expressing visions of members of the “Futures” group. The series, which concludes in the May 25 issue, is accompanied by a blog, The Futures of School Reform, written by the group. Readers are invited to participate by posting comments on the blog, or writing letters to the editor.
The second scenario might be called “controlled engagement,” or “frog gets a GPS device.” In this case, schools make some nonincremental leaps in the way they are organized and run. 69��ý set the learning destinations and map out the best pathways to those destinations. Technology becomes less about adult control and rationalizing business operations and more about opening portals for learning that are connected to the world outside of schools. So, for example, an elementary school in Huntsville, Ala., develops a two-way bilingual instructional cooperative to teach its students Mandarin with an elementary school in Shanghai, where teachers alternate lessons in English and Mandarin using video technology and shared materials. Or a rural high school in South Dakota is wired into a math-science collaborative sponsored by the that connects its students to a physics course with students from several other high schools around the country, including in New York City and in San Diego. Teachers are less gatekeepers of knowledge, and more knowledge brokers. School leaders become less managers of instruction, and more entrepreneurs connecting their organizations to the broader learning environment. 69��ý become less places where students go to learn from adults, and more places where adults and students get together to enter a broader learning environment. But schools still play an important role in determining what constitutes “knowledge” and “learning” for students.
The third scenario might be called “open access to learning,” or “caterpillar learns to fly.” Here schools cease to play the determining role in what constitutes knowledge and learning. If society (read: politicians) decides that there has to be such a role (which will inevitably be increasingly contested), that role is vested in an organization that sets broad standards for content (not unlike the common-core standards) and broad guidance about how students and parents can get access to learning consistent with those standards. 69��ý are on their own, competing with other types of service providers and learning modalities for the interest and loyalty of students and their parents. A family might combine services from two or three different organizations into a learning plan for its children—tutoring for “basic” academic content, active learning and access to the digital environment at an experiential learning center, and physical and kinesthetic development from a sports and recreation center. Over time, a student might choose to focus for a period on only one type of learning—six months in an intensive language program, or three months on a biology expedition. And students might also choose to work on some areas of learning exclusively through online vendors. 69��ý would accumulate digital learning portfolios that would summarize their learning and proficiency around broad standards and would be available for higher education institutions and potential employers to access. The system would be financed by a per-student capitation grant, adjusted to family income, parents’ education, and student learning needs (which would include accommodations for disabilities and English-language learning). 69��ý, as we presently know them, would gradually cease to exist and be replaced by social networks organized around the learning goals of students and their families.
The authors of this commentary and other members of the Futures of School Reform Group will expand upon and discuss their visions for the future of schools in an Education Week blog.
Which of these environments makes sense, given the future of learning in our society? Is “school” a brick-and-mortar building, or a way of organizing and providing access and support for learning? Who decides what and how to learn? What is society’s role in that decisionmaking? How do we ensure that the students who have the most to gain and lose in any fundamental transformation of “school”—the very students least well served by the current institution of school—are best supported to thrive and succeed?
Here are a few first steps to get a start in exploring these questions:
1. Talk with students, teachers, and other educators about what school could and should look like. Encourage them to be audaciously imaginative.
2. Visit (in person or virtually) schools that look really different.
3. Use new school construction and renovation conversations as opportunities to think differently about the design of learning environments.
It’s 2025. What does school look like? Or better yet, what does learning look like and sound like?